Fabulous Info About Why Do We Use Stacks Instead Of Arrays 3 Axes Graph
An array is used to hold things that will later be accessed sequentially or through the index.
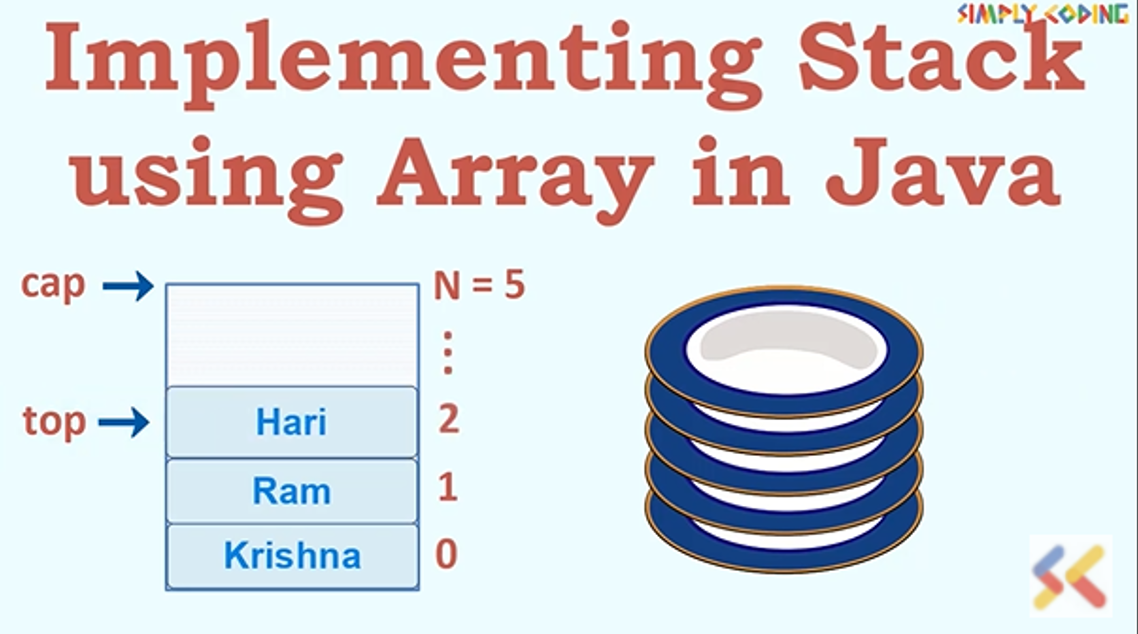
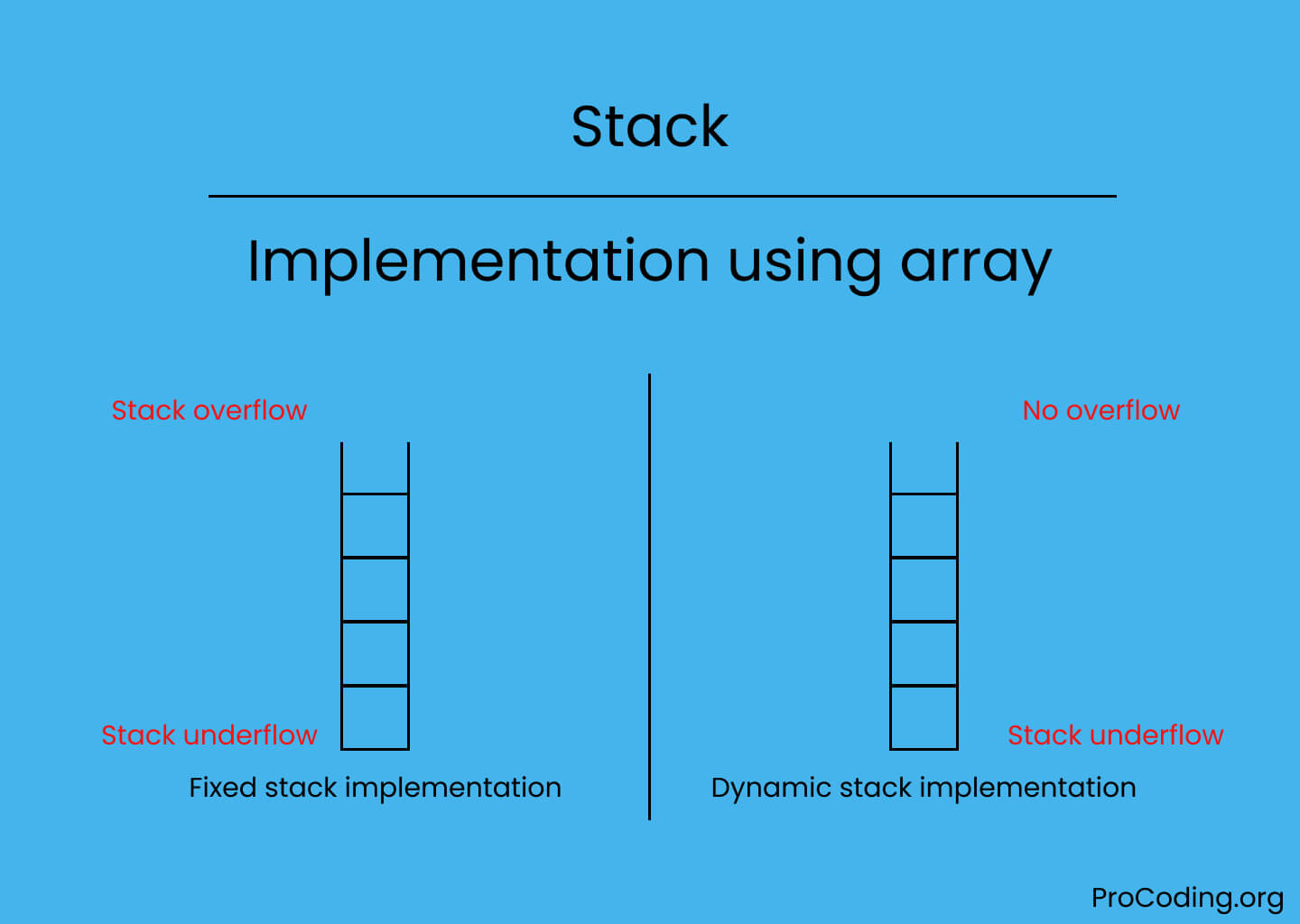
Why do we use stacks instead of arrays. It isn't an alternative to an array, but just another (more abstract) way of talking about the array and the specific access pattern needed for this task. A stack is an abstract data type that consists of a predefined capacity. Stacks are popular, linear data structures — or more abstractly a sequential collection.
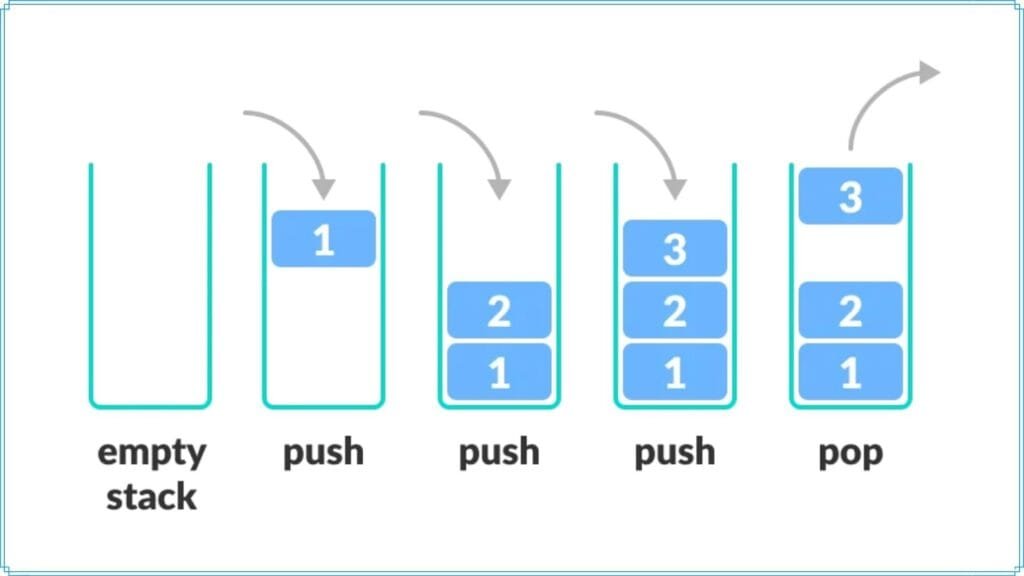
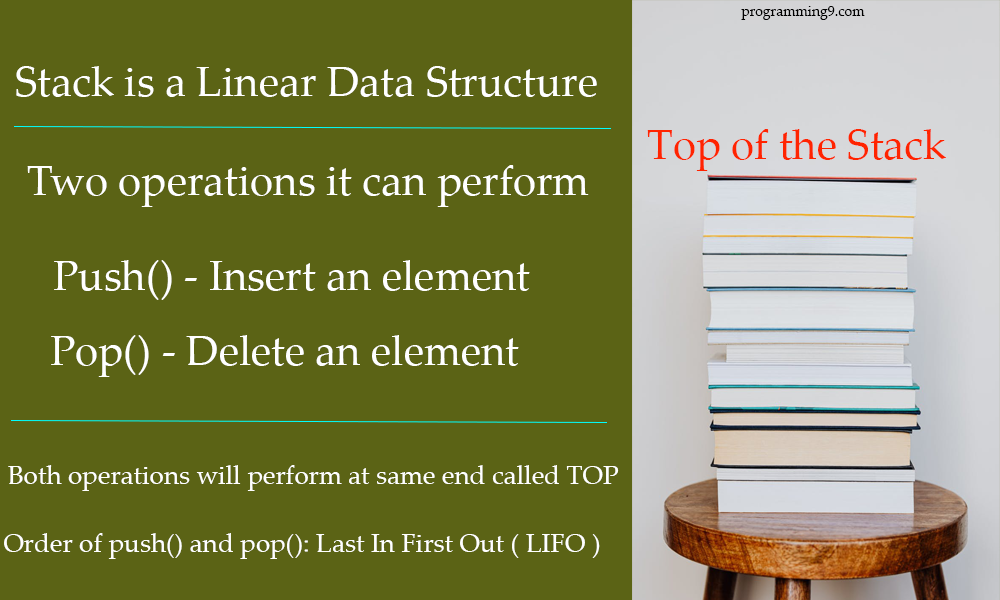
Before diving into the rabbit hole, it’s best to understand the reasons why you might want to consider a stack or queue rather than an array. In a stack, the new element is always inserted at the top position. When programmers say stack, they are talking about which data goes.
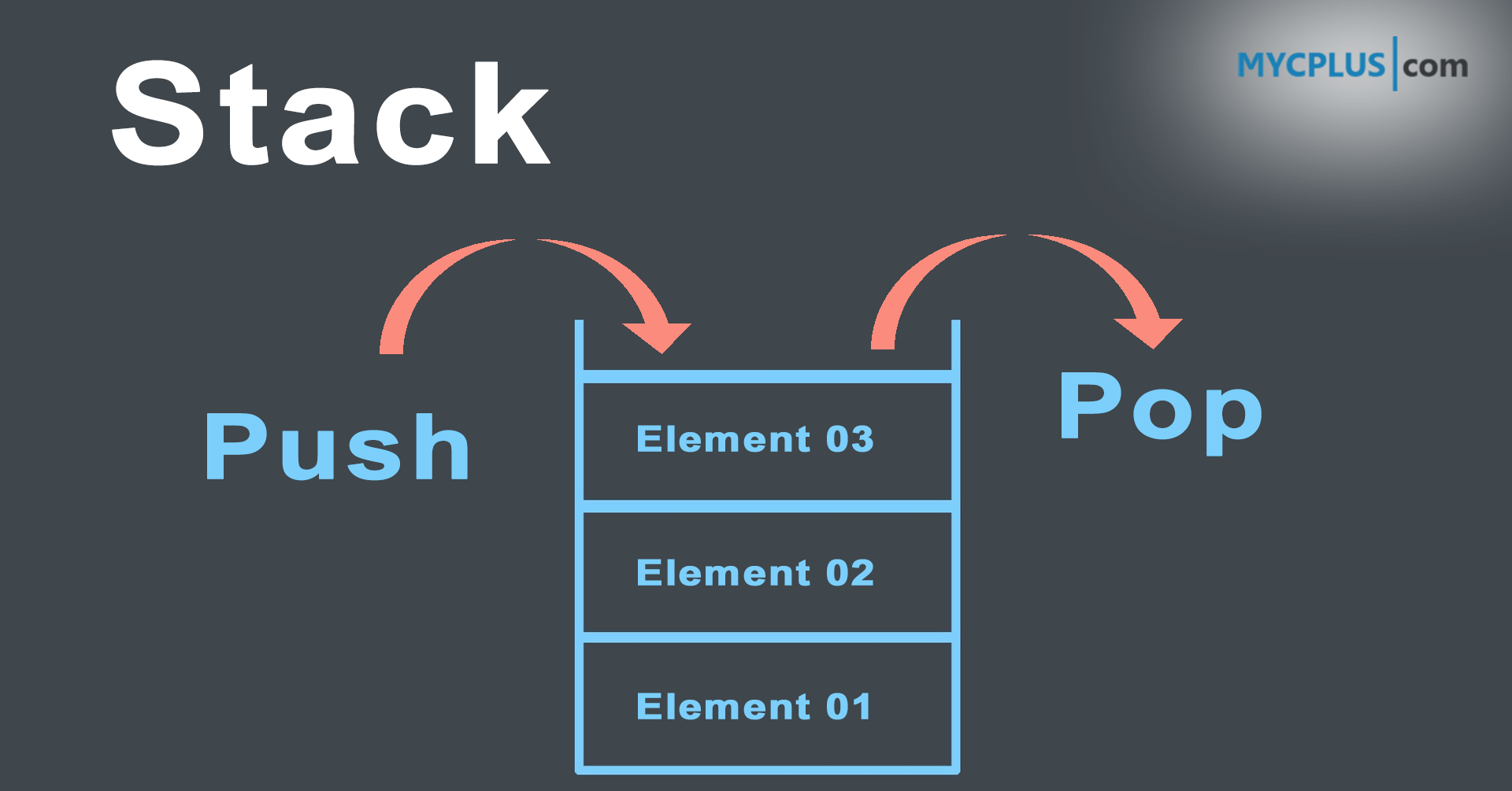
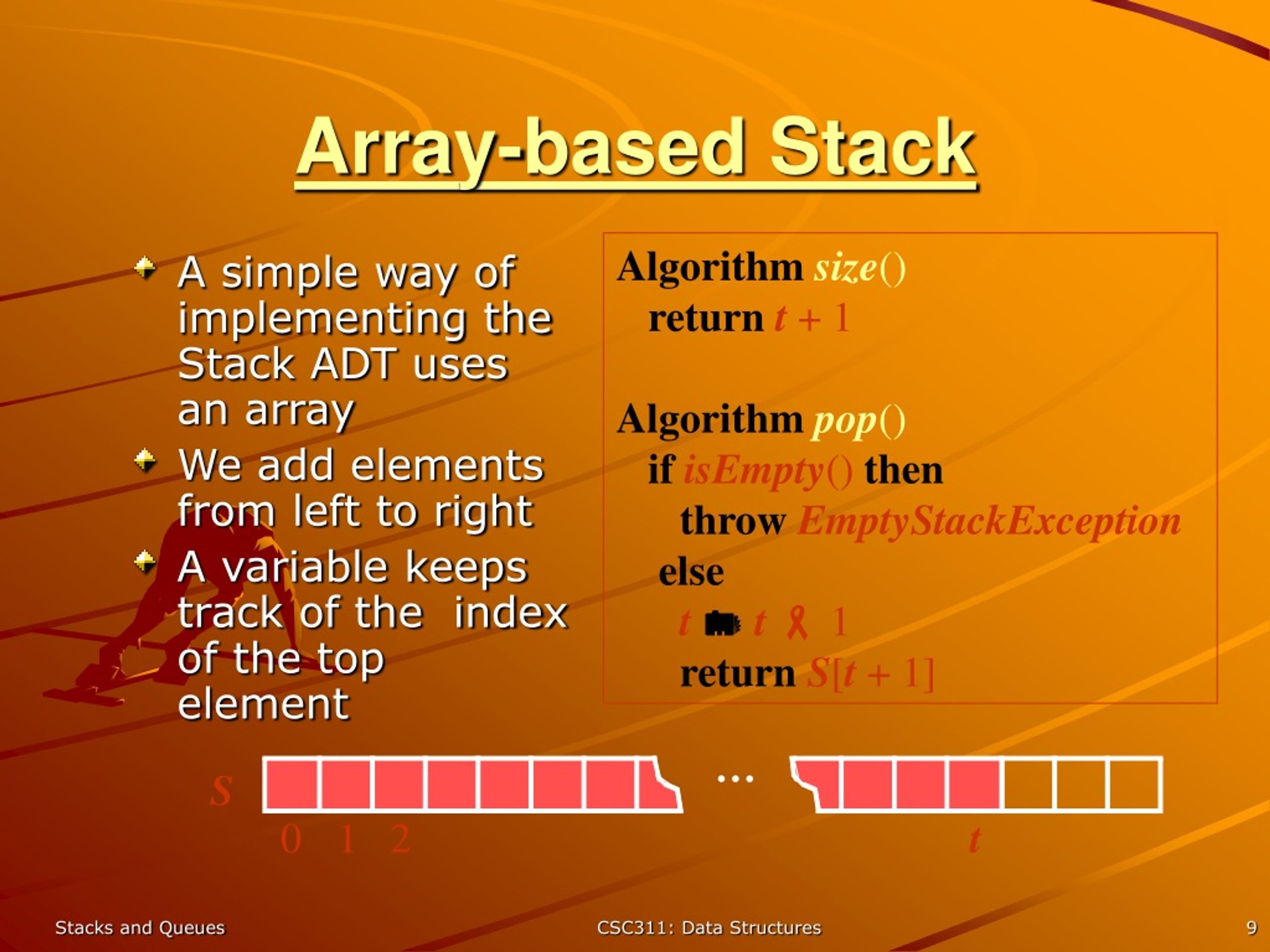
The data structure doesn't imply any sort of access method (fifo, lifo, filo,. In a stack, push() is a function used to insert an element into the stack. The implementation of queues and stacks using resizing arrays (from lecture) consumes between ~8n and ~32n bytes of memory for a stack/queue containing n items (~8n in.
Why don't we use queues and. How to implement a stack? Stacks can be implemented using two main approaches:
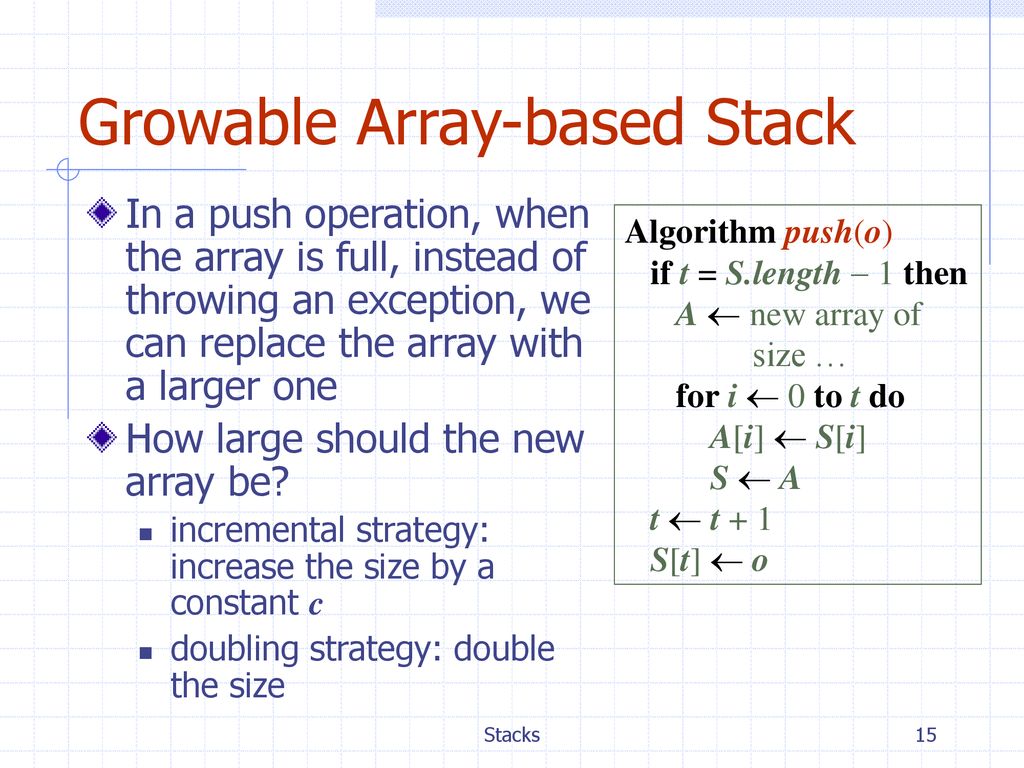
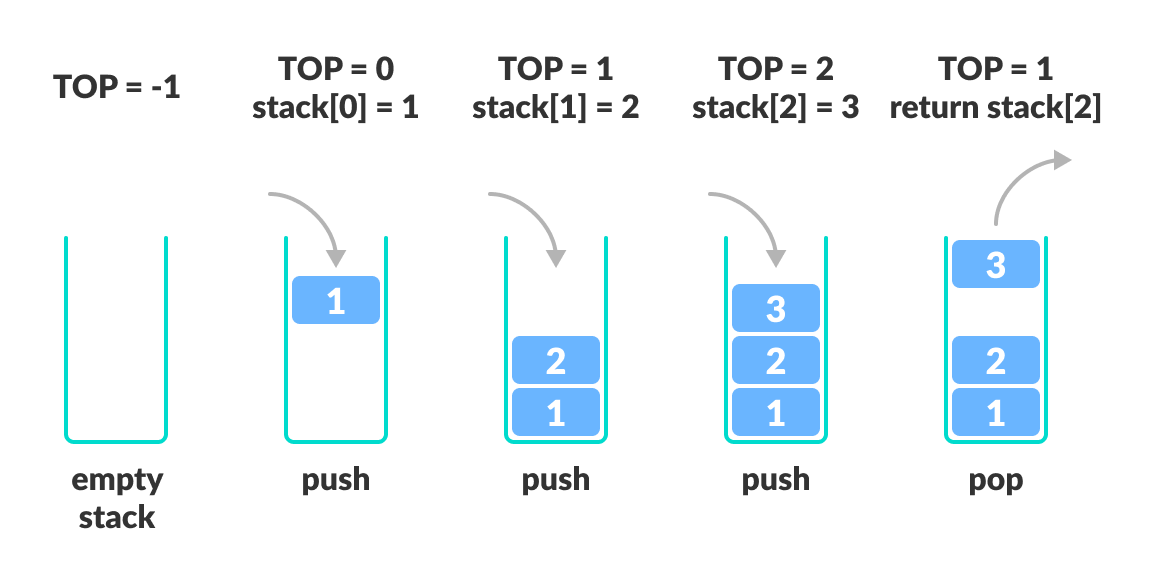
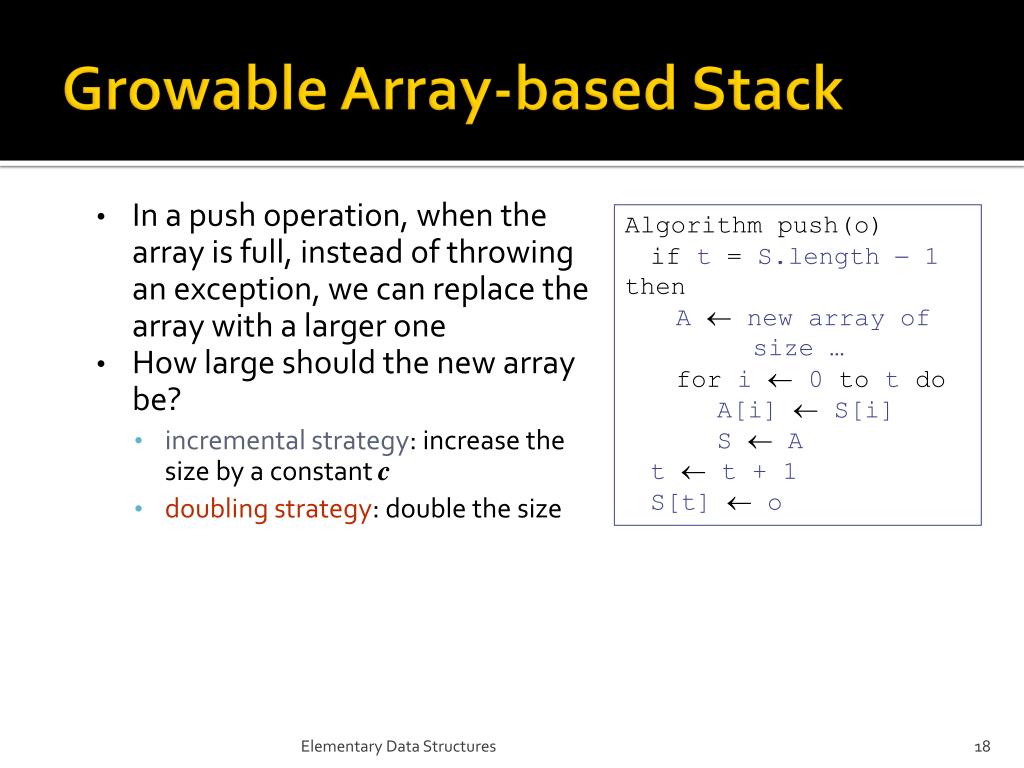
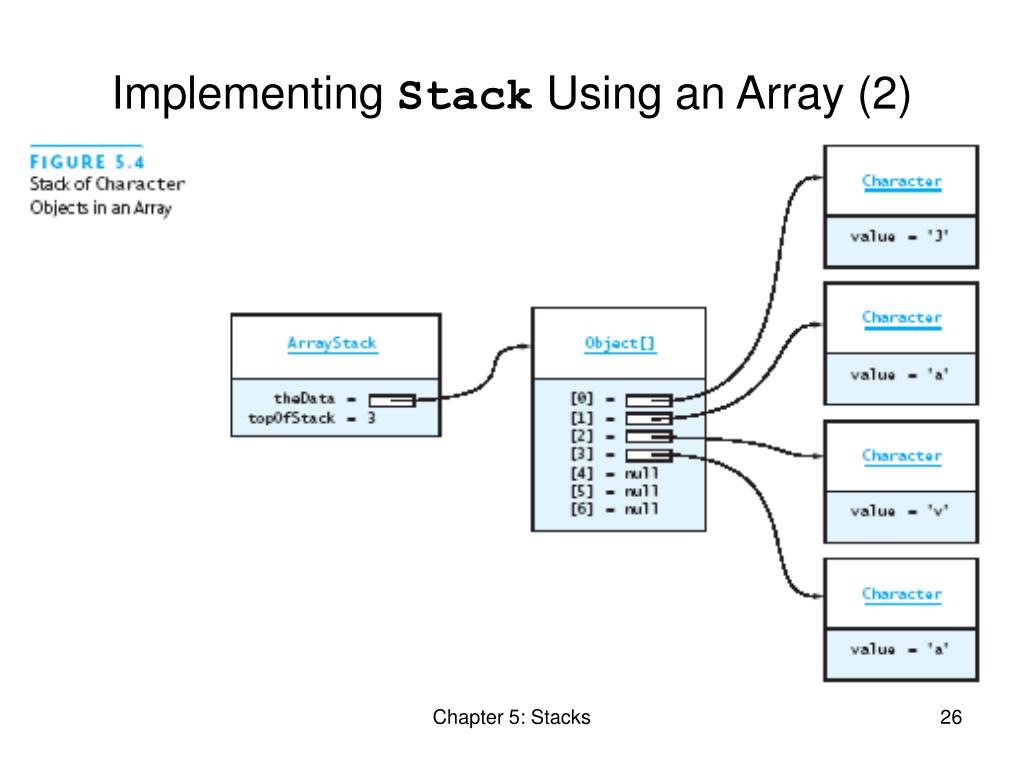
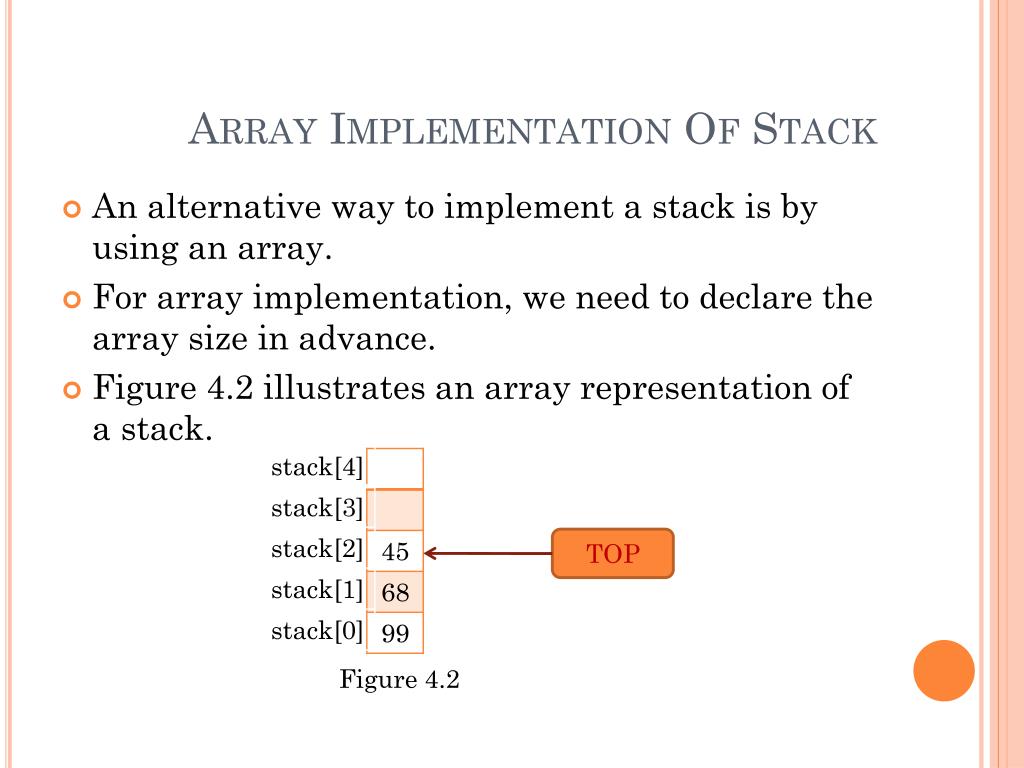
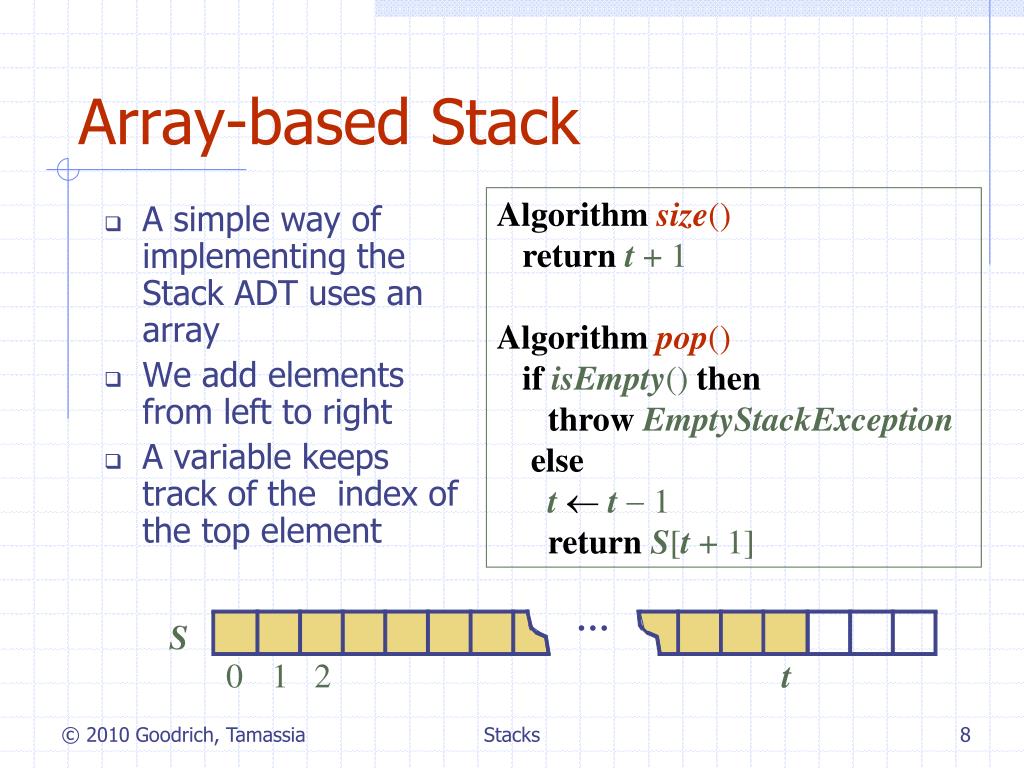
Because it's easier to think in terms of data structure operations rather than the mechanics of working with an array. There are two principle operations involved with stack; To implement a stack using an array, initialize an array and treat its end as the stack’s top.
Rust has been stack overflow’s most loved language for four years in a row and emerged as a compelling language choice for both backend and system developers, offering a. Higher level data structures, such as hashtables, stacks and queues, all may use an array (or multiple arrays) internally, while linked lists and binary trees. In this dsa tutorial, we'll
It allows adding and removing elements in a particular order. Arrays offer fast access to elements, but their size is. Array is simply a sequence of objects stored contiguously.
Let’s see how we can implement each operation on the stack utilizing the array data structure. In the case of a queue, there are two ends, rear and front for insertion and deletion respectively. Write once, debug, and then use it.
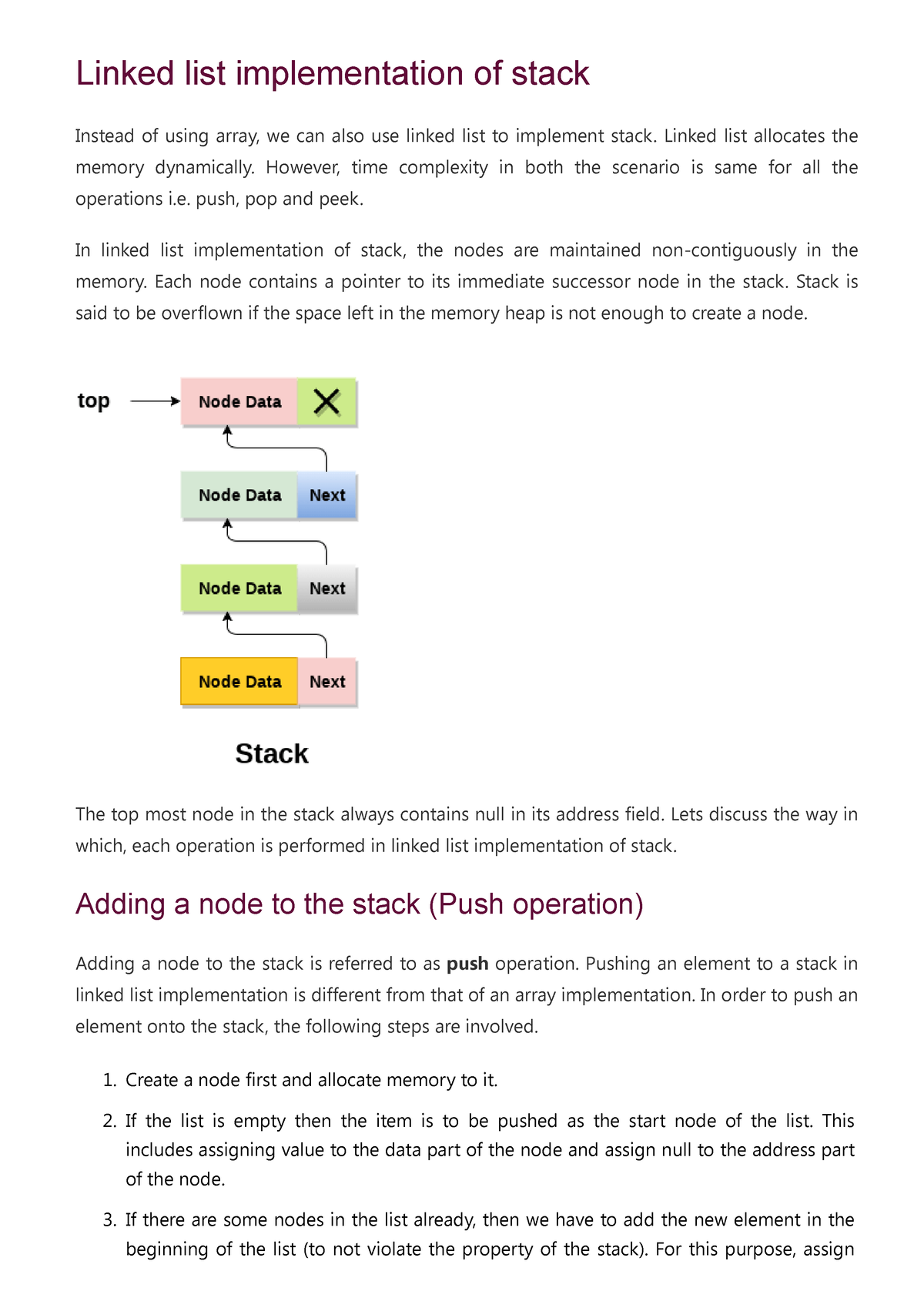
Array and list structures provide a description of how the data is stored, along with guarantees of the complexity of fundamental operations on the structures. A linked list is a data type similar to an array, but it is not indexed, unlike an array. If you know that a stack will never exceed a dozen entries, it might be more efficient to allocate an array and keep track of the index of the last entry (a stack.