Lessons I Learned From Info About How Do You Know If Its Discrete Or Continuous To Change The Axis Data In Excel
In an introductory stats class, one of the first things you’ll learn is the difference between discrete vs continuous variables.
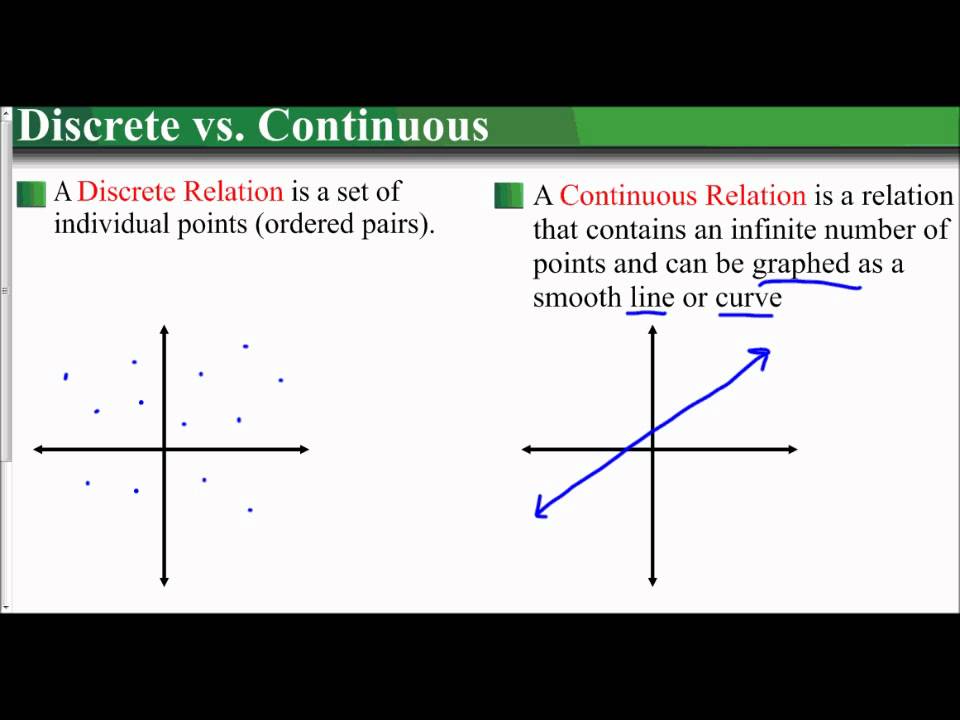
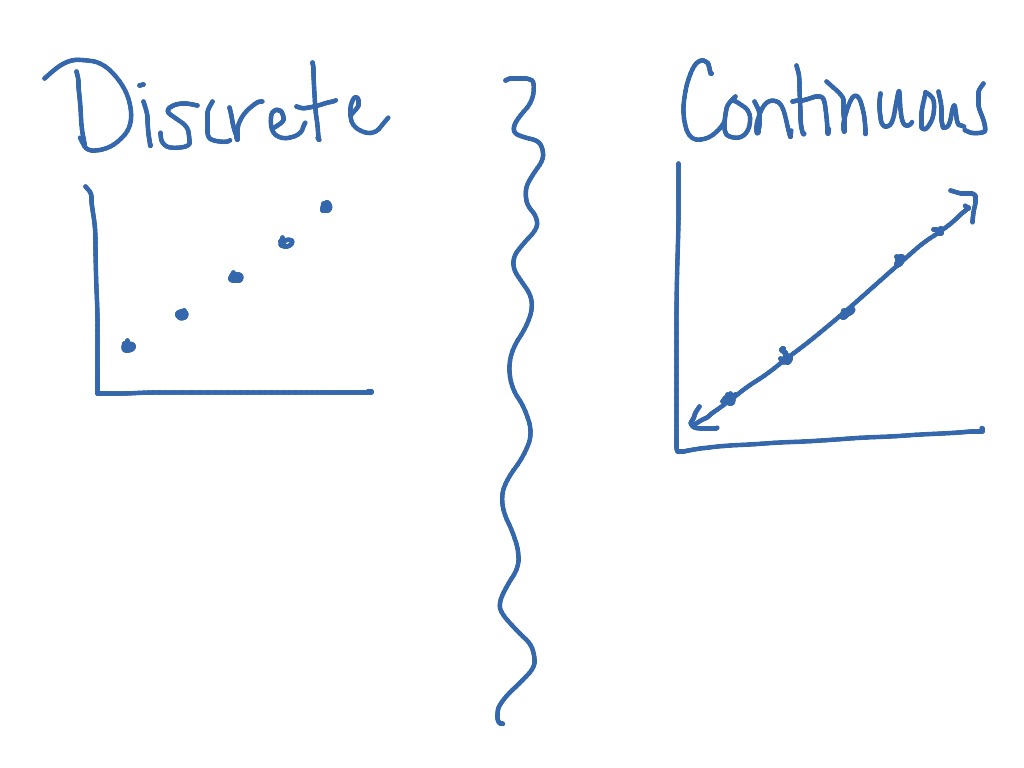
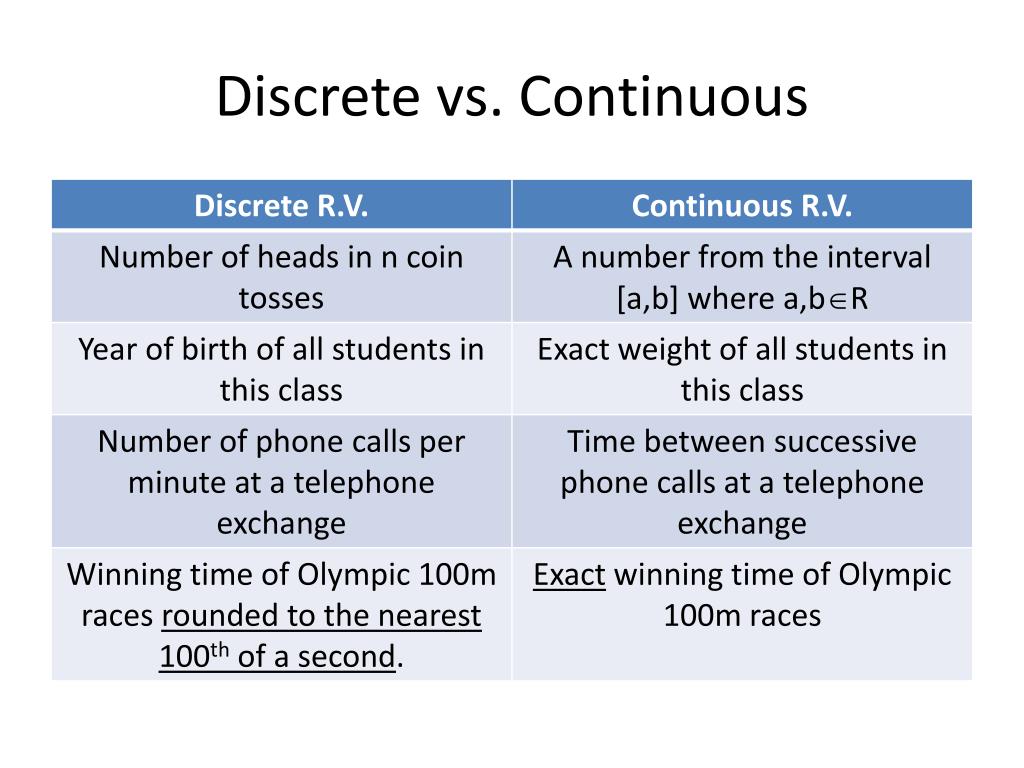
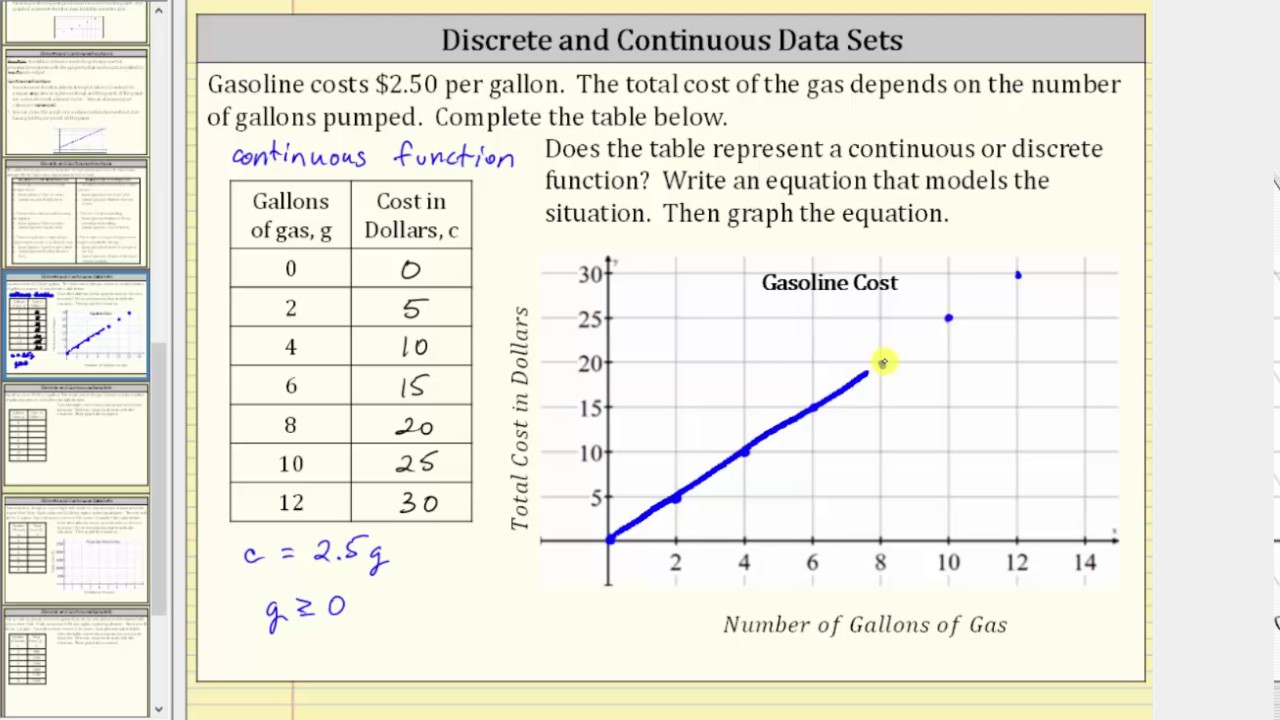
How do you know if its discrete or continuous. In a nutshell, discrete variables are points plotted on a chart and a continuous variable can be plotted as a line. Understanding the properties of both types is crucial in many statistical applications. Could be any value (within the range of human heights), not just certain fixed heights,
When you have a numeric variable, you need to determine whether it is discrete or continuous. Continuous and discrete graphs visually represent functions and series, respectively. Continuous random variables, on the other hand, can take on any value in a given interval.
How to display graphically continuous data? I’ll explain the differences and provide examples of discrete vs continuous data. Discrete variable assumes independent values whereas continuous variable assumes any value in a given range or continuum.
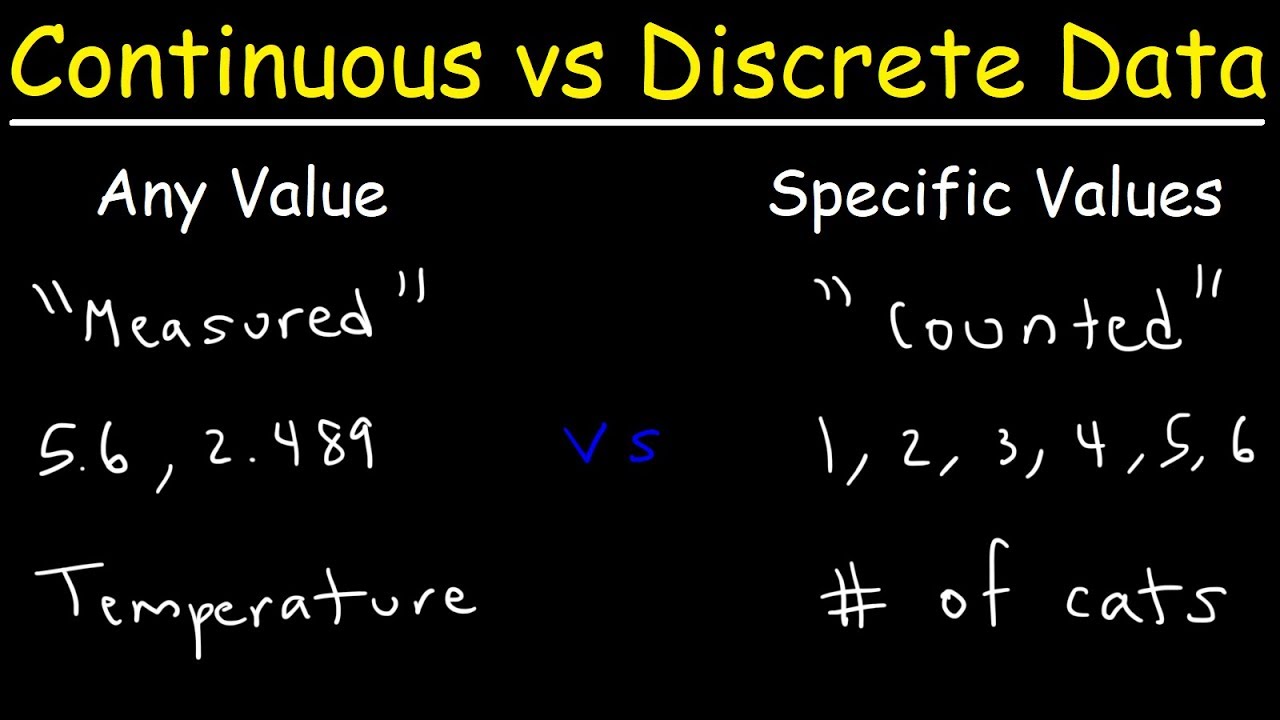
Discrete random variables take on countable, specific values, while continuous random variables assume uncountably infinite values. In fields like data analytics and data science, which often require advanced math, it’s vital to understand the nature, structure, and. All data are measured with finite precision, so all data is technically discrete (whether or not the process from which the data arise is discrete or continuous).
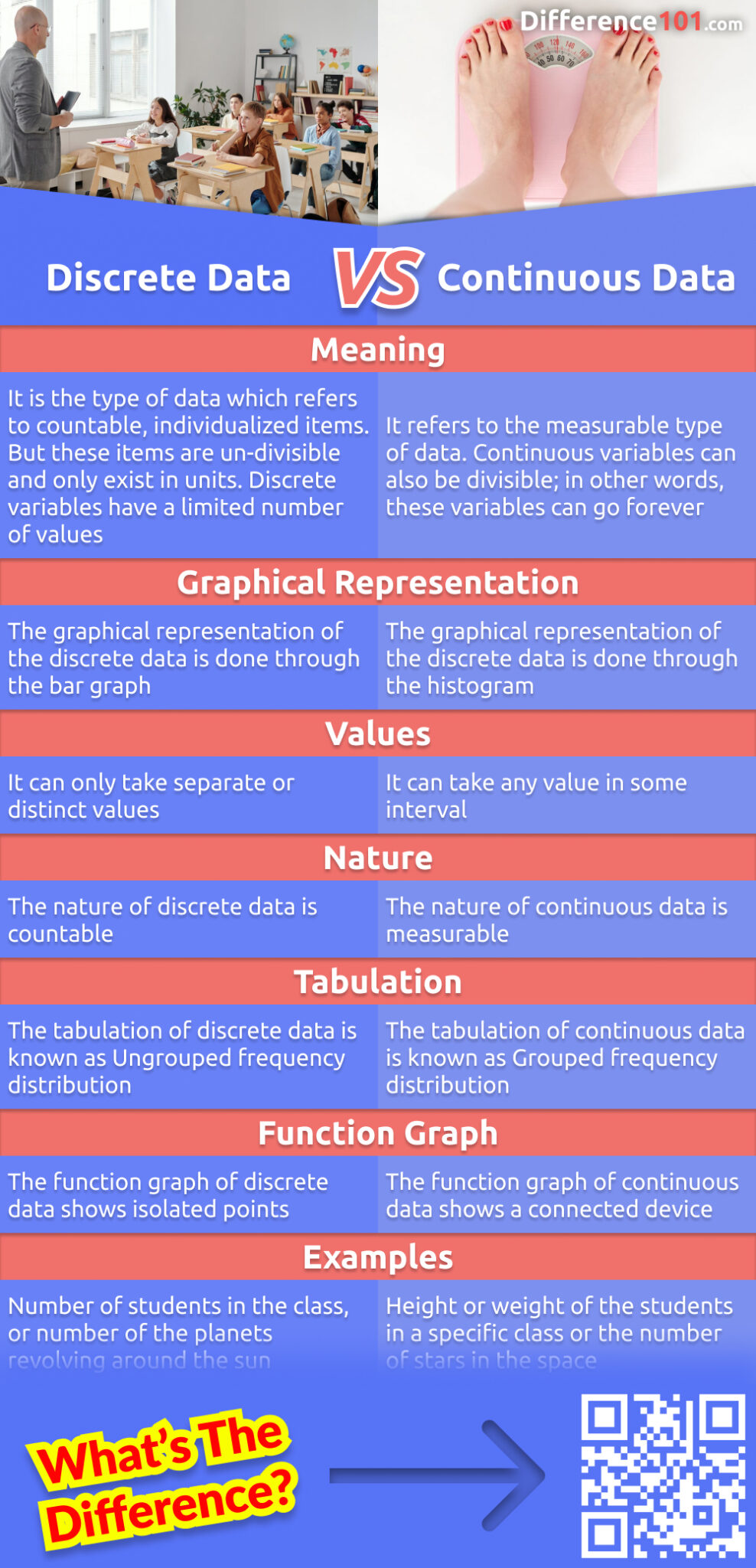
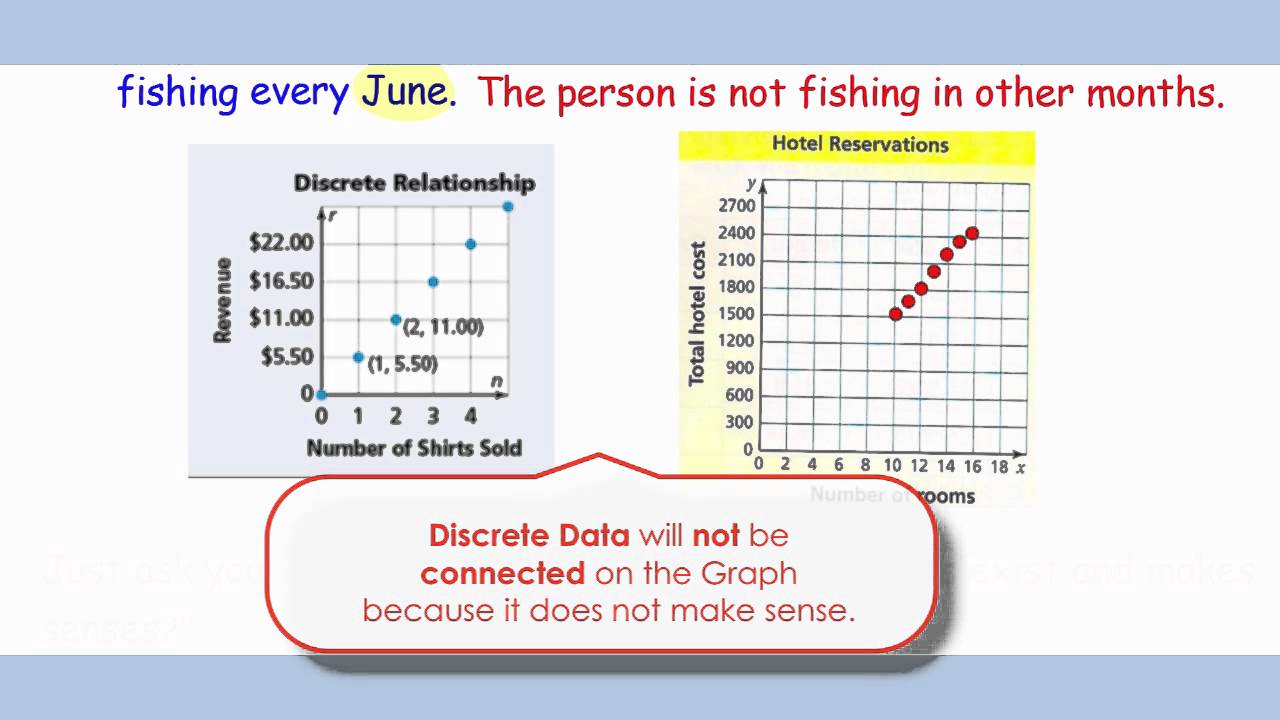
Discrete data points are distinct, separate and countable, while continuous data points are part of a continuous spectrum. What is the difference between continuous and discrete data? Discrete data is often referred to as categorical data, whereas continuous data is referred to as numerical data.
It gives plenty of examples and practice problems with gra. Discrete data is countable while continuous — measurable. Continuous data is data that falls in a constant sequence.
Continuous data encompasses a range of values, such as height or temperature, depicted using histograms or line graphs, allowing for detailed. In broad strokes, the critical factor is the following: A good common rule for defining if a data is continuous or discrete is that if the point of measurement can be reduced in half and still make sense, the data is continuous.
Though these graphs perform similar functions, their properties are not interchangeable. How data were collected and how variables were recorded will likely give you some clues about that; The main difference between discrete data and continuous data is that discrete data is data collected for a discrete random variable, while continuous data is data collected for a continuous random variable.
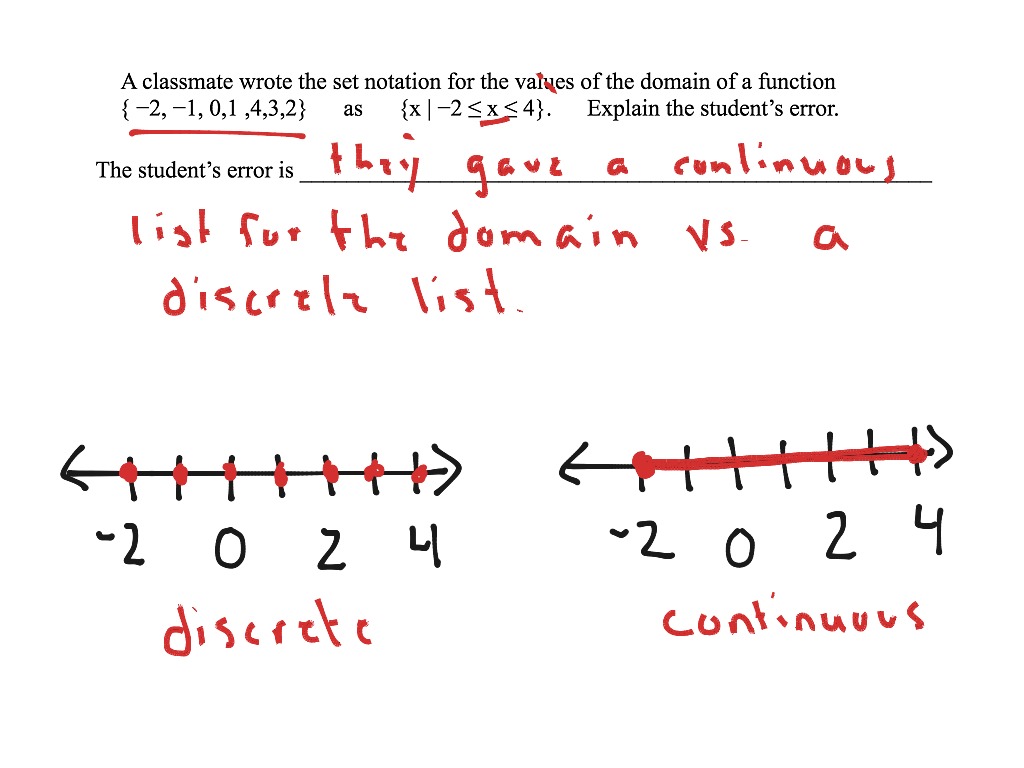
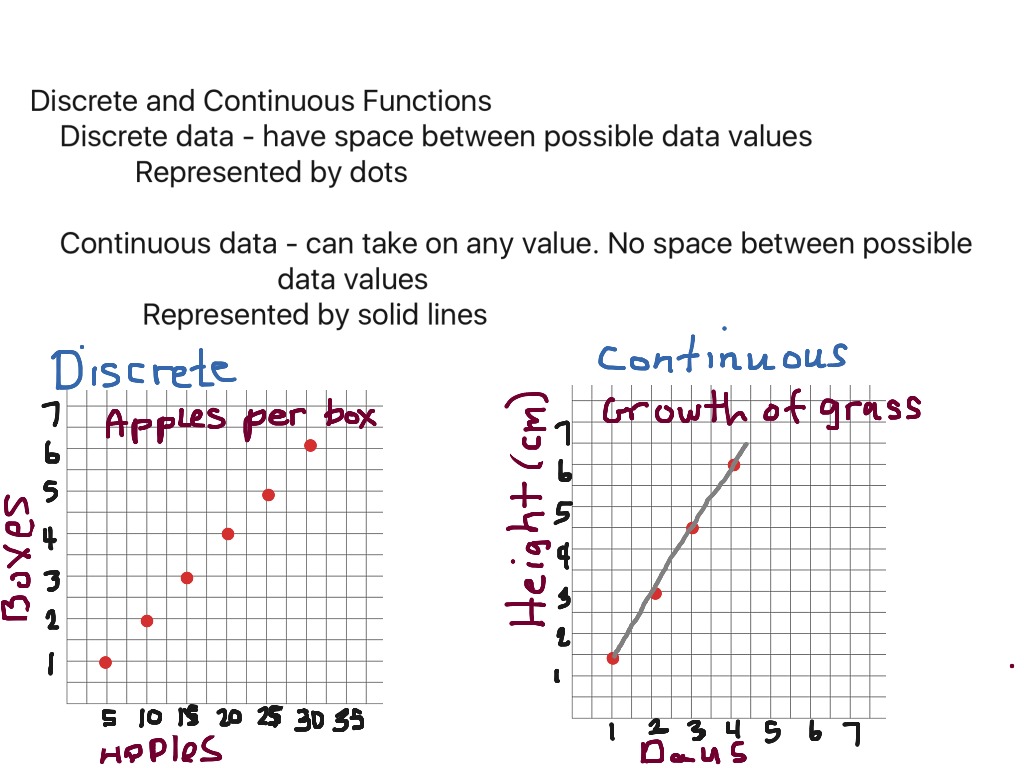
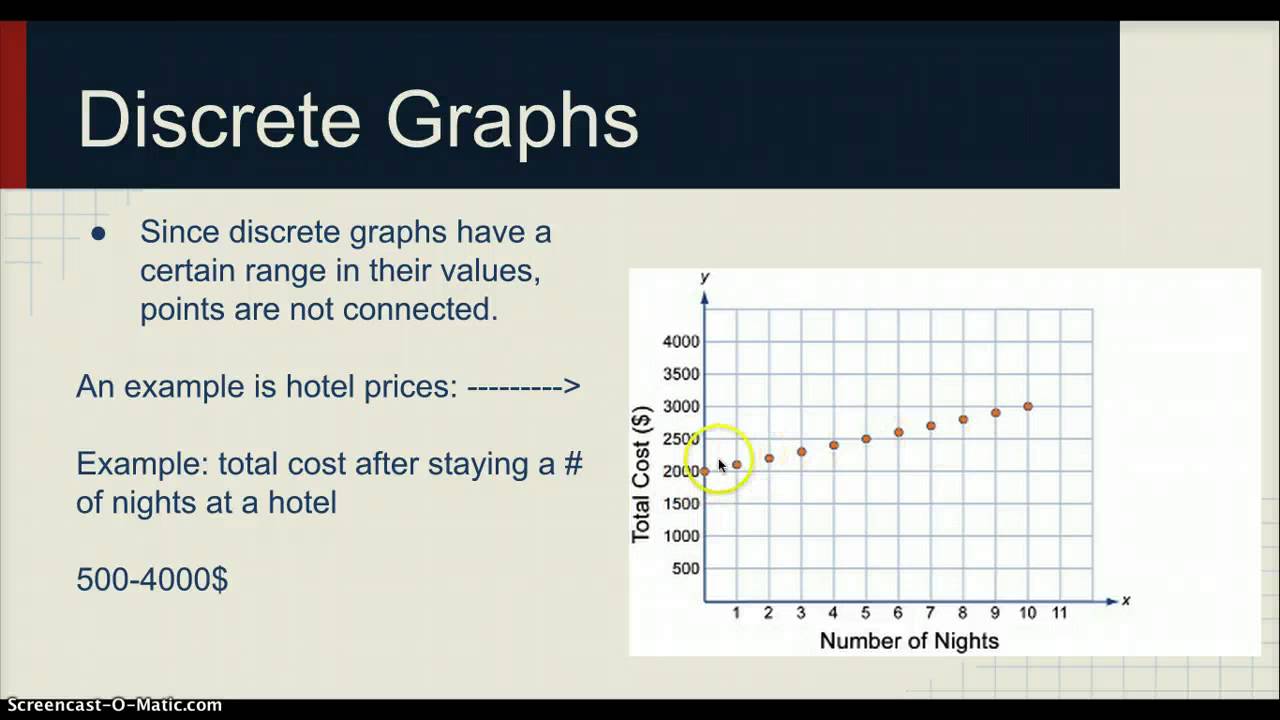
In addition, it is likely to depend on whether you want to model your data as continuous or discrete ones (see e.g., question related to likert items and discrete scales analysis). Discrete data is the type of data that has clear spaces between values. A discrete variable can be graphically represented by isolated points.
Discrete and continuous variables are two types of quantitative variables: Discrete and continuous data. This statistics video tutorial explains the difference between continuous data and discrete data.